Crowdsourcing is an example of innovation that has revolutionized the way organizations access ideas and perspectives, fostering collaboration and driving innovation across various industries. By leveraging the collective knowledge and expertise of a distributed crowd, crowdsourcing empowers organizations to tap into a vast pool of diverse viewpoints, leading to breakthrough solutions and transformative outcomes.
The key characteristics of crowdsourcing include its open and distributed nature, allowing anyone with an internet connection to participate; its focus on idea generation and problem-solving; and its reliance on technology platforms to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Definition of Crowdsourcing

Crowdsourcing is a form of collaborative problem-solving and innovation that involves soliciting contributions from a large group of people, typically via an open call or online platform.
Key characteristics of crowdsourcing include:
- Open and distributed:Contributions are sought from a wide range of individuals, regardless of their location or background.
- Task-based:Crowdsourcing projects typically involve specific tasks or challenges that contributors can complete.
- Incentivized:Contributors are often motivated by rewards, such as payment, recognition, or the satisfaction of contributing to a shared goal.
Examples of successful crowdsourcing projects include:
- The Linux operating system, developed through open-source collaboration.
- The SETI@home project, which harnessed the idle processing power of millions of computers to search for extraterrestrial signals.
- Innocentive, a platform that connects companies with individuals who can solve specific scientific and technical challenges.
Crowdsourcing as a Form of Innovation
Crowdsourcing enables access to a wider pool of ideas and perspectives, fostering innovation by:
- Tapping into diverse expertise:Crowdsourcing allows organizations to leverage the knowledge and skills of a global community, expanding the range of potential solutions.
- Promoting collaboration and knowledge sharing:Crowdsourcing platforms facilitate communication and collaboration among contributors, leading to the cross-fertilization of ideas and the development of innovative solutions.
- Driving innovation in various industries:Crowdsourcing has been successfully applied in fields such as product design, software development, scientific research, and marketing.
Benefits of Crowdsourcing for Innovation
Crowdsourcing offers several advantages for innovation, including:
- Increased creativity and diversity of ideas:Crowdsourcing taps into the collective wisdom of a large and diverse group of contributors, leading to a broader range of innovative solutions.
- Cost-effectiveness:Crowdsourcing can be a cost-effective way to access expertise and solve problems, compared to traditional methods such as hiring consultants or conducting in-house research.
- Speed and efficiency:Crowdsourcing platforms enable organizations to quickly and efficiently gather ideas and solutions from a global community.
Challenges of Crowdsourcing for Innovation
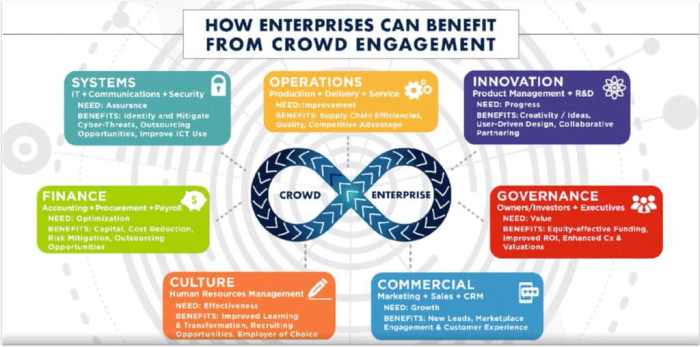
Crowdsourcing for innovation also presents potential drawbacks and challenges:
- Data quality:Managing and ensuring the quality of contributions from a large number of individuals can be challenging.
- Intellectual property:Crowdsourcing raises concerns about protecting the intellectual property rights of contributors and organizations.
- Managing large crowds:Effectively managing and engaging a large number of contributors can be complex and time-consuming.
Strategies for overcoming these challenges include:
- Establishing clear guidelines:Providing clear instructions and guidelines to contributors helps ensure data quality and consistency.
- Implementing quality control mechanisms:Using tools and processes to review and validate contributions helps mitigate data quality issues.
- Respecting intellectual property:Establishing clear policies and agreements regarding the ownership and use of contributions addresses intellectual property concerns.
- Engaging effectively with contributors:Building a strong community and providing ongoing support to contributors helps manage large crowds effectively.
Best Practices for Crowdsourcing Innovation: Crowdsourcing Is An Example Of Innovation
| Planning | Execution | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Define clear goals and objectives | Use a robust crowdsourcing platform | Track and measure results |
| Identify and engage target audience | Set clear guidelines and incentives | Gather feedback and iterate |
| Structure tasks effectively | Facilitate collaboration and communication | Recognize and reward contributors |
Case Studies of Crowdsourcing Innovation
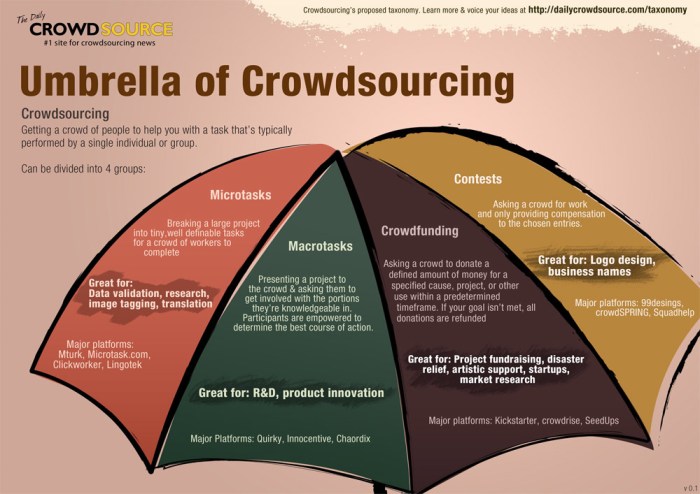
Several companies and organizations have successfully used crowdsourcing for innovation:
- Lego:The Lego Ideas platform allows users to submit and vote on new product ideas, leading to the development of innovative products such as the Lego Architecture series.
- Netflix:Netflix used a crowdsourcing competition to develop a more accurate movie recommendation algorithm, resulting in significant improvements in user satisfaction.
- Innocentive:Innocentive has facilitated the development of breakthrough solutions for challenges in various industries, including healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Query Resolution
What are the key benefits of crowdsourcing for innovation?
Crowdsourcing offers several benefits for innovation, including access to a wider pool of ideas and perspectives, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing, and reducing the cost and time associated with traditional innovation processes.
What are the challenges associated with crowdsourcing for innovation?
Potential challenges of crowdsourcing for innovation include managing large crowds, ensuring data quality, protecting intellectual property, and addressing issues related to motivation and engagement.
What are the best practices for effective crowdsourcing innovation?
Best practices for effective crowdsourcing innovation include careful planning, clear communication, effective crowd management, ongoing evaluation, and continuous improvement.