Embark on an enlightening journey into the captivating world of evolution and selection with the evolution and selection pogil answer key as your guide. This comprehensive resource unlocks the secrets of natural selection, empowering you to unravel the intricate tapestry of life’s evolutionary history.
Delve into the profound concept of evolution by natural selection, uncovering its transformative power in shaping the diversity of species. Witness the profound impact of genetic variation, the driving force behind evolutionary change. Explore the dynamic interplay between selective pressure and evolution, unraveling the mechanisms that mold populations.
Evolution
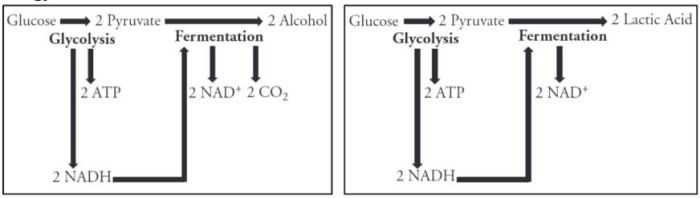
Evolution is the process by which the genetic composition of a population changes over generations. It is driven by natural selection, which is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals with favorable traits in a particular environment.
Natural selection acts on genetic variation within a population. Individuals with traits that are better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous genes to their offspring. Over time, this leads to a gradual shift in the genetic makeup of the population, resulting in the evolution of new species or the adaptation of existing ones.
Selective Pressure
Selective pressure is the force that drives evolution. It arises from the environment and acts on individuals within a population. Selective pressure can be biotic (e.g., competition for resources, predation) or abiotic (e.g., temperature, rainfall).
Types of Selection, Evolution and selection pogil answer key
There are three main types of selection:
- Directional selectionfavors individuals with extreme traits in one direction. This can lead to the evolution of larger or smaller body size, faster running speeds, or other traits that provide an advantage in the current environment.
- Stabilizing selectionfavors individuals with intermediate traits. This helps to maintain a stable population mean, reducing the variance in trait values. Stabilizing selection is common for traits that are essential for survival, such as body temperature or blood pressure.
- Disruptive selectionfavors individuals with extreme traits in both directions. This can lead to the evolution of two or more distinct phenotypes within a population. Disruptive selection is often seen in environments with contrasting selective pressures, such as a forest edge where both camouflage and speed are advantageous.
FAQ Resource: Evolution And Selection Pogil Answer Key
What is the fundamental principle of evolution by natural selection?
Evolution by natural selection posits that individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their favorable genes to future generations.
How does genetic variation contribute to evolution?
Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, introducing diversity into populations and enabling the survival of individuals best suited to their environment.
What are the different types of selection?
Selection can be directional, favoring one extreme of a trait; stabilizing, maintaining the average trait value; or disruptive, favoring both extremes of a trait.