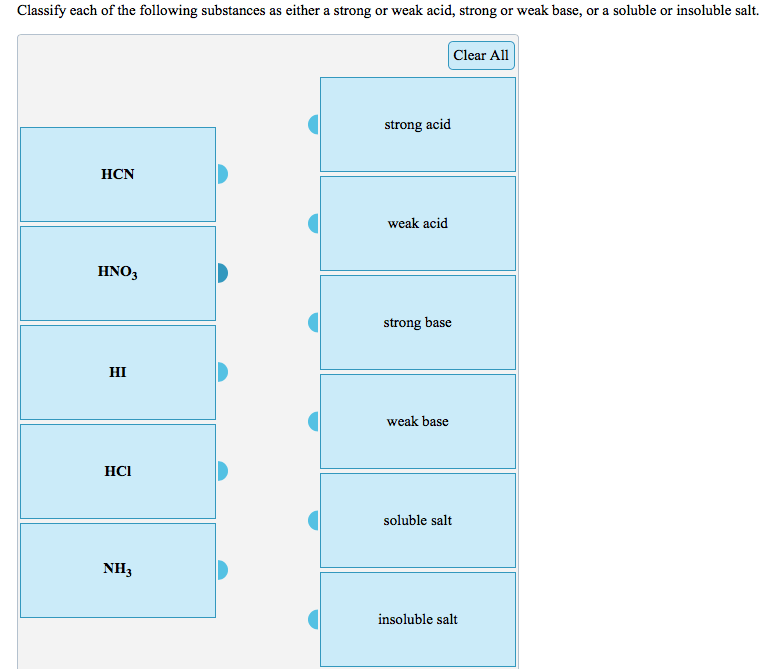
Classify each of the following acids as strong or weak. Delve into the fascinating realm of acid chemistry as we explore the properties, behaviors, and factors that determine the strength of acids. From the highly reactive strong acids to the less dissociative weak acids, this exploration unveils the fundamental principles governing acid behavior.
Acids, ubiquitous in our world, play crucial roles in various chemical reactions and industrial processes. Understanding their strength is paramount in predicting their reactivity and applications. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed examination of acid strength, empowering you with the knowledge to classify acids accurately and unravel their chemical mysteries.
Classification of Acids: Classify Each Of The Following Acids As Strong Or Weak.
Acids are chemical compounds that donate protons (H+ ions) in a chemical reaction. They can be classified as either strong or weak based on their ability to dissociate in water.
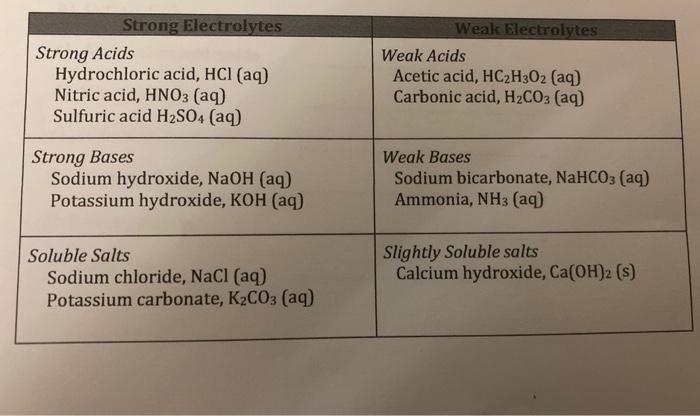
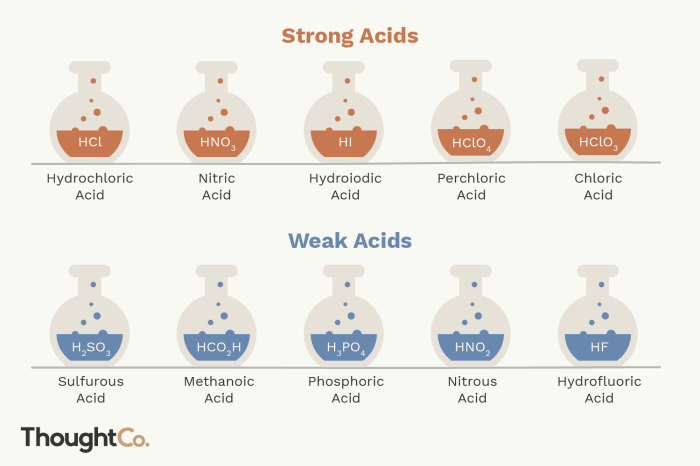
Strong Acids
Strong acids are acids that completely dissociate in water, releasing all of their protons. They have a dissociation constant (Ka) of 1 or greater.
- Examples of strong acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3).
- Strong acids are corrosive and can cause severe burns.
Weak Acids
Weak acids are acids that only partially dissociate in water, releasing only a small fraction of their protons. They have a dissociation constant (Ka) of less than 1.
- Examples of weak acids include acetic acid (CH3COOH), carbonic acid (H2CO3), and hydrofluoric acid (HF).
- Weak acids are less corrosive than strong acids and cause less severe burns.
Classification of Acids Table
| Acid | Formula | Strength | Dissociation Constant (Ka) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | HCl | Strong | 1 |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | Strong | 1 |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 | Strong | 1 |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | Weak | 1.8 x 10^-5 |
| Carbonic acid | H2CO3 | Weak | 4.3 x 10^-7 |
| Hydrofluoric acid | HF | Weak | 3.5 x 10^-4 |
Factors Affecting Acid Strength, Classify each of the following acids as strong or weak.
The strength of an acid is affected by several factors, including:
- Bond strength:Acids with weaker bonds between the hydrogen and the rest of the molecule are stronger acids.
- Electronegativity:Acids with more electronegative atoms are stronger acids.
- Resonance:Acids with resonance structures are weaker acids.
- Solvation:Acids that are more easily solvated by water are stronger acids.
FAQ Explained
What is the key difference between strong and weak acids?
Strong acids dissociate completely in water, releasing all their hydrogen ions, while weak acids dissociate partially, releasing only a small fraction of their hydrogen ions.
How does acid strength affect chemical reactions?
Strong acids react more vigorously and completely than weak acids due to their higher concentration of hydrogen ions, which are responsible for chemical reactivity.
What factors influence the strength of an acid?
The strength of an acid is influenced by factors such as the stability of its conjugate base, the electronegativity of the acidic atom, and the size of the molecule.