Introducing the six types of chemical reaction worksheet, an invaluable tool for understanding the fundamental principles of chemistry. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of chemical reactions, their characteristics, and practical applications.
Chemical reactions play a crucial role in our everyday lives, from the digestion of food to the combustion of fuels. By exploring the six main types of chemical reactions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of matter and its transformations.
Introduction
A chemical reaction is a process that involves the rearrangement of atoms or ions to form new substances. Chemical reactions are essential for life and occur all around us, from the digestion of food to the burning of fuels.
Examples of common chemical reactions include:
- Rusting of iron
- Burning of wood
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
Types of Chemical Reactions: Six Types Of Chemical Reaction Worksheet
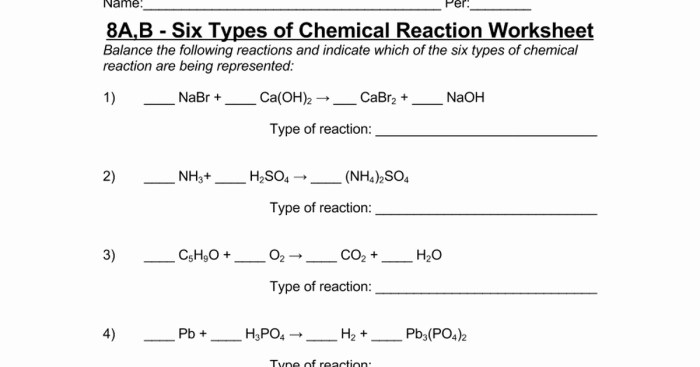
There are six main types of chemical reactions:
- Synthesis: Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition: A single substance breaks down into two or more products.
- Single-displacement: An element replaces another element in a compound.
- Double-displacement: Two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.
- Combustion: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
- Acid-base: An acid and a base react to form a salt and water.
Balancing Chemical Equations
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction. Balanced chemical equations show the number of atoms of each element that are involved in the reaction. To balance a chemical equation, coefficients are added to the reactants and products so that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
For example, the following unbalanced equation shows the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
H2+ O 2→ H 2O
This equation is unbalanced because there are four hydrogen atoms on the left side of the equation but only two on the right side. To balance the equation, a coefficient of 2 is added to the water molecule:
H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
Now the equation is balanced because there are four hydrogen atoms on both sides of the equation.
Reaction Rates and Equilibrium
The rate of a chemical reaction is the speed at which the reactants are converted into products. Many factors can affect the rate of a reaction, including the concentration of the reactants, the temperature, and the presence of a catalyst.
Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products do not change over time. At equilibrium, the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at the same rate.
Applications of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Medicine: Chemical reactions are used to produce drugs, vaccines, and other medical treatments.
- Industry: Chemical reactions are used to produce plastics, fertilizers, and other industrial products.
- Everyday life: Chemical reactions are used in everything from cooking to cleaning to generating electricity.
FAQ Guide
What are the six main types of chemical reactions?
The six main types of chemical reactions are synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, combustion, and acid-base.
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation, reflecting the law of conservation of mass.
How do chemical reactions affect our daily lives?
Chemical reactions are essential for many everyday processes, such as cooking, cleaning, and the production of medicines and materials.